20.2 字符串的常用成员
我们主要研究的字符串类型的成员包括构造函数、成员方法、属性以及字段。
❑构造函数:
String类型有8个构造函数,我们这里介绍其中常用的3个,如表20-1所示。
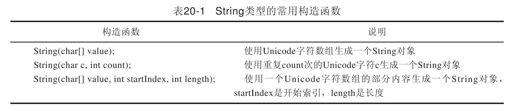
我们分别使用上述各个构造函数来生成String实例对象,如代码清单20-2所示。
代码清单20-2 使用多个构造函数生成String对象
using System;
namespace ProgrammingCSharp4
{
class StringSample
{
public static void Main()
{
char[]c=new char[]{'h','e','l','l','o','','w','o','r','l','d','!'};
string s1=new string(c);
string s2=new string('1',5);
string s3=new string(c,6,5);
Console.WriteLine(s1);
Console.WriteLine(s2);
Console.WriteLine(s3);
}
}
}
上述代码的运行结果为:
hello world!
11111
world
请按任意键继续……
❑成员方法
String类的成员方法非常多,很多方法都有多个重载版本,我们不能一一介绍其中的每个方法,只能挑一些重点的方法进行介绍。其中有多个重载版本的只选择其中1~2个具有代表性的方法进行介绍;另外有些方法的参数为char类型,有时还有一个对应的string参数版本,这时选择string参数的版本。String类有许多方法成员都是静态的,我们也对此进行了区分并说明,如表20-2所示。
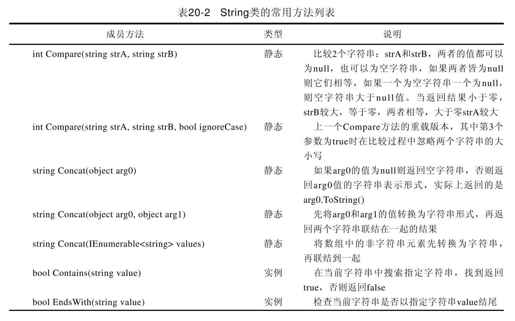

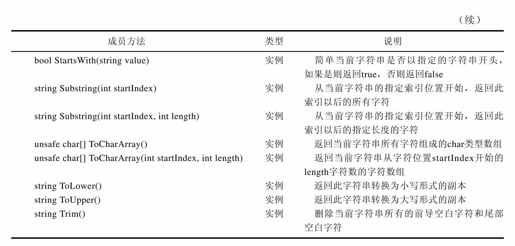
我们在代码清单20-3中演示了String类的常用方法的使用示例。
代码清单20-3 String类的常用方法的使用示例
using System;
namespace ProgrammingCSharp4
{
class StringSample
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Compare(null,null));
Console.WriteLine(string.Compare("a","b"));
Console.WriteLine(string.Concat(10));
Console.WriteLine(string.Concat(10,20));
Console.WriteLine(string.Concat(new object[]{1,"a",3}));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Contains("c"));
Console.WriteLine("abc".EndsWith("c"));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Equals((object)"abc"));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Equals("abc"));
Console.WriteLine(string.Equals("abc","abcd"));
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1},{2}",new string[]{"a","b","c"});
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}!","world");
Console.WriteLine("abc".IndexOf("c"));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Insert(1,"8"));
Console.WriteLine(string.Intern("abcd"));
string s1="a";
s1+="bcde";
Console.WriteLine(string.IsInterned(s1)??"Null");
string s2=new string('',10);//空白字符串
Console.WriteLine(string.IsNullOrEmpty(s2));
Console.WriteLine(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(s2));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",",1,2,3));
Console.WriteLine("abca".LastIndexOf("a"));
Console.WriteLine("a".PadLeft(10));
Console.WriteLine("a".PadLeft(10,'-'));
Console.Write("a".PadRight(10));
Console.WriteLine("b");
Console.WriteLine("a".PadRight(10,'-'));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Replace("c","cde"));
string[]strs="a,b,c-d,e-fg".Split(',','-');
foreach(string s in strs)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
Console.WriteLine("abc".StartsWith("a"));
Console.WriteLine("abc".Substring(1,1));
char[]chars="abc".ToCharArray();
char[]chars2="abc".ToCharArray(0,2);
Console.WriteLine("abc".ToUpper());
Console.WriteLine("ABC".ToLower());
Console.WriteLine("abc".Trim());
}
}
}
上述代码的运行结果如下:
0
-1
10
1020
1a3
True
True
True
True
False
a,b,c
Hello,world!
2
a8bc
abcd
Null
False
True
1,2,3
3
a
————-a
a
b
a————-
abcde
a
b
c
d
e
fg
True
b
ABC
abc
abc
请按任意键继续……
❑属性
String类的属性只有两个,它们是Chars和Length,关于它们的介绍如表20-3所示。
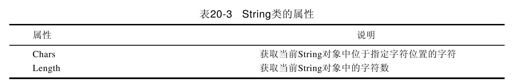
其中需要说明的是,访问Chars属性需要通过索引器,我们只需使用“变量名[索引]”的形式即可取得指定索引位置的字符。Length属性是字符串中的字符数组的长度,也对应着指定字符串是由多少个字符组成的,因此可以使用Length属性是否为0来判断一个字符串是否为空。更完整的示例,请参考代码清单20-4。
代码清单20-4 String属性使用示例
using System;
namespace ProgrammingCSharp4
{
class StringSample
{
public static void Main()
{
string s1="abc";
for(int i=0;i<s1.Length;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(s1[i]);
}
}
}
}
上述代码的运行结果如下:
a
b
c
请按任意键继续……
❑字段
String类只有一个公共字段:Empty,它是静态和只读的,因此它的值和实例无关。它的值始终为“”。注意,空(null)和空白(“”)是不同的,字符串的值为空白字符,并不代表字符串的值为空,空代表什么也没有,代码清单20-5说明了这一点。
代码清单20-5 String类的Empty字段示例
using System;
namespace ProgrammingCSharp4
{
class StringSample
{
public static void Main()
{
string s1=string.Empty;
s1=s1.PadLeft(10);
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(s1))
{
Console.WriteLine(“s1是空字符串”);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(“s1不是空字符串”);
}
if(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(s1))
{
Console.WriteLine(“s1是空白字符”);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(“s1不是空白字符”);
}
}
}
}
上述代码的运行结果为:
s1不是空字符串
s1是空白字符
请按任意键继续……
