28.1.2 访问Python代码
要访问Python代码,先要配置环境,步骤如下:
(1)访问IronPython的官方网站(http://ironpython.codeplex.com/),下载IronPython并安装,如图28-3所示;
(2)新建一个控制台类型的应用程序,如图28-4所示;
(3)将IronPython安装目录下的两个程序集添加到新建的工程的引用中,如图28-5所示,这两个程序集如下:
❑\IronPython 2.6 for.NET 4.0\IronPython.dll
❑\IronPython 2.6 for.NET 4.0\Microsoft.Scripting.dll
图 28-3 IronPython官方网站
图 28-4 新建控制台类型的应用程序
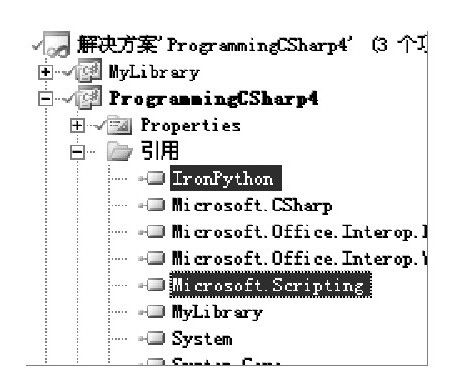
图 28-5 添加对IronPython的引用
编写一段Python代码,保存于c:\Calculator.py,如代码清单28-3所示。
代码清单28-3 Calculator.py的代码
def Add(a,b):
return a+b
接下来是关键,编写C#代码访问该Python代码,如代码清单28-4所示。
代码清单28-4 在C#中访问Python代码
using System;
using IronPython.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Scripting.Hosting;
namespace ProgrammingCSharp4
{
class DynamicSample
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Loading Calculator.py……");
//声明并初始化一个ScriptRuntime对象
ScriptRuntime py=Python.CreateRuntime();
//返回动态对象calculator,我们不知道它的具体类型,只知道
//它有哪些操作成员
dynamic calculator=py.UseFile(@"c:\Calculator.py");
Console.WriteLine("loaded\n");
int x=18,y=24;
//向动态对象calculator发出动态调用Add,编译时并
//不检查该操作是否存在,在运行时才会进行检查
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}\n",x,y,answer1);
decimal s=40.9M,t=1.1M;
decimal answer2=calculator.Add(s,t);
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}\n",s,t,answer2);
string p="Forty-",q="two";
string answer3=calculator.Add(p,q);
Console.WriteLine("\"{0}\"+\"{1}\"=\"{2}\"\n",p,q,answer3);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
int answer1=calculator.Add(x,y);
上述代码的运行结果为:
Loading Calculator.py……loaded
18+24=42
40.9 +1.1=42.0
"Forty-"+"two"="Forty-two"
请按任意键继续……
