28.5.6 结账
当用户点击购物车的"Go to Checkout"按钮时,将触发checkout.php脚本。该结账脚本及其后面的脚本必须通过SSL访问到,但是,我们给出的示例应用程序并不要求这么做(要了解更多关于SSL的信息,请参阅第18章“通过PHP和MySQL实现安全事务”)。
结账页面如图28-8所示。
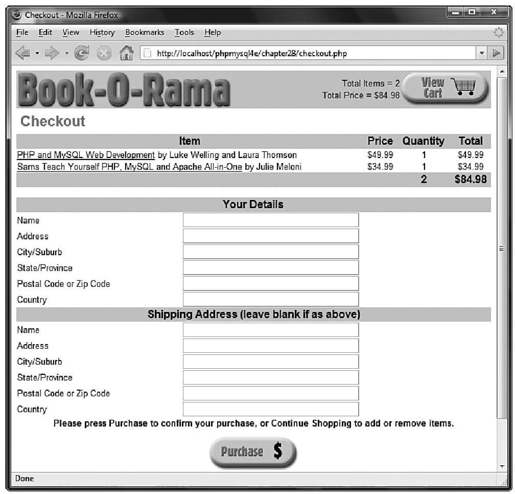
图 28-8 checkout.php脚本获取顾客的详细信息
结账脚本要求顾客输入地址(如果运送地址与该地址不同,需要输入运送地址)。该脚本非常简单,其代码如程序清单28-13所示。
程序清单28-13 checkout.php——该脚本获取用户的详细信息
<?php
//include our function set
include('book_sc_fns.php');
//The shopping cart needs sessions,so start one
session_start();
do_html_header("Checkout");
if(($_SESSION['cart'])&&(array_count_values($_SESSION['cart']))){
display_cart($_SESSION['cart'],false,0);
display_checkout_form();
}else{
echo"<p>There are no items in your cart</p>";
}
display_button("show_cart.php","continue-shopping","Continue Shopping");
do_html_footer();
?>
在以上脚本中,并没有什么奇怪的事情发生。如果购物车是空的,脚本将通知该用户;否则,它将显示如图28-8所示的表单。
如果用户继续点击该表格下面的"Purchase"按钮,将进入purchase.php脚本。在图28-9中,可以看到该脚本的输出。
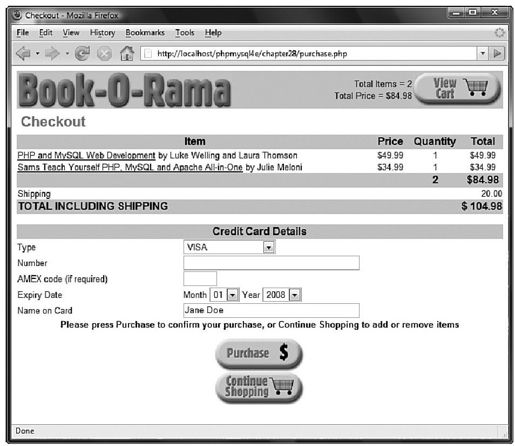
图 28-9 purchase.php脚本计算客户购买的商品数量和最终的订单价格,并且获得客户的付款详细信息
以上脚本代码比checkout.php脚本逻辑稍微复杂一些,如程序清单28-14所示。
程序清单28-14 purchase.php——该脚本将用户订单的详细信息保存到数据库中并获取付款细节
<?php
include('book_sc_fns.php');
//The shopping cart needs sessions,so start one
session_start();
do_html_header("Checkout");
//create short variable names
$name=$_POST['name'];
$address=$_POST['address'];
$city=$_POST['city'];
$zip=$_POST['zip'];
$country=$_POST['country'];
//if filled out
if(($_SESSION['cart'])&&($name)&&($address)&&($city)
&&($zip)&&($country)){
//able to insert into database
if(insert_order($_POST)!=false){
//display cart,not allowing changes and without pictures
display_cart($_SESSION['cart'],false,0);
display_shipping(calculate_shipping_cost());
//get credit card details
display_card_form($name);
display_button("show_cart.php","continue-shopping","Continue Shopping");
}else{
echo"<p>Could not store data,please try again.</p>";
display_button('checkout.php','back','Back');
}
}else{
echo"<p>You did not fill in all the fields,please try again.</p><hr/>";
display_button('checkout.php','back','Back');
}
do_html_footer();
?>
以上代码的逻辑简单明了:它首先检查用户是否填好了表单,并调用insert_order()函数,这是一个简单的函数,将用户填写的详细信息插入数据库。其代码如程序清单28-15所示。
该函数相当长,因为我们需要插入用户所有的细节,包括订单细节以及他们要买的每一本书的细节。
程序清单28-15 order_fns.php文件中的insert_order()函数——该函数将所有的用户订单详细信息插入到数据库中
<?php
function process_card($card_details){
//connect to payment gateway or
//use gpg to encrypt and mail or
//store in DB if you really want to
return true;
}
function insert_order($order_details){
//extract order_details out as variables
extract($order_details);
//set shipping address same as address
if((!$ship_name)&&(!$ship_address)&&(!$ship_city)
&&(!$ship_state)&&(!$ship_zip)&&(!$ship_country)){
$ship_name=$name;
$ship_address=$address;
$ship_city=$city;
$ship_state=$state;
$ship_zip=$zip;
$ship_country=$country;
}
$conn=db_connect();
//we want to insert the order as a transaction
//start one by turning off autocommit
$conn->autocommit(FALSE);
//insert customer address
$query="select customerid from customers where
name='".$name."'and address='".$address."'
and city='".$city."'and state='".$state."'
and zip='".$zip."'and country='".$country."'";
$result=$conn->query($query);
if($result->num_rows>0){
$customer=$result->fetch_object();
$customerid=$customer->customerid;
}else{
$query="insert into customers values
('','".$name."','".$address."','".$city."',
'".$state."','".$zip."','".$country."')";
$result=$conn->query($query);
if(!$result){
return false;
}
}
$customerid=$conn->insert_id;
$date=date("Y-m-d");
$query="insert into orders values
('','".$customerid."','".$_SESSION['total_price']."',
'".$date."','".PARTIAL."','".$ship_name."',
'".$ship_address."','".$ship_city."',
'".$ship_state."','".$ship_zip."',
'".$ship_country."')";
$result=$conn->query($query);
if(!$result){
return false;
}
$query="select orderid from orders where
customerid='".$customerid."'and
amount>(".$_SESSION['total_price']."-.001)and
amount<(".$_SESSION['total_price']."+.001)and
date='".$date."'and
order_status='PARTIAL'and
ship_name='".$ship_name."'and
ship_address='".$ship_address."'and
ship_city='".$ship_city."'and
ship_state='".$ship_state."'and
ship_zip='".$ship_zip."'and
ship_country='".$ship_country."'";
$result=$conn->query($query);
if($result->num_rows>0){
$order=$result->fetch_object();
$orderid=$order->orderid;
}else{
return false;
}
//insert each book
foreach($_SESSION['cart']as$isbn=>$quantity){
$detail=get_book_details($isbn);
$query="delete from order_items where
orderid='".$orderid."'and isbn='".$isbn."'";
$result=$conn->query($query);
$query="insert into order_items values
('".$orderid."','".$isbn."',".$detail['price'].",$quantity)";
$result=$conn->query($query);
if(!$result){
return false;
}
}
//end transaction
$conn->commit();
$conn->autocommit(TRUE);
return$orderid;
}
?>
插入操作的不同部分被包括在一个事务中,它以如下语句开始:
$conn->autocommit(FALSE);
以如下语句结束:
$conn->commit();
$conn->autocommit(TRUE);
这是应用程序中唯一需要使用事务的地方。如何避免在其他情况下也使用它呢?请查看db_connect()函数的代码,如下所示:
function db_connect(){
$result=new mysqli('localhost','book_sc','password','book_sc');
if(!$result){
return false;
}
$result->autocommit(TRUE);
return$result;
}
很明显,以上代码与在其他章节中使用的相同函数名称的代码不同。在创建了到MySQL的连接后,必须开启自动提交模式。
正如我们前面介绍的,这可以确保每一个SQL语句将自动被提交。当需要使用一个多语句事务时,必须关闭自动提交模式,执行一系列的插入操作,提交数据,然后再重新启用自动提交模式。
然后我们根据顾客地址计算出运送费用,并通过如下所示代码告诉他们需要的费用:
display_shipping(calculate_shipping_cost());
在这里,我们使用的calculate_shipping_cost()函数将始终返回$20。当真正建立一个购物网站的时候,必须选择一个送货方式,计算出不同的目的地需要的运送费用,并据此计算出总费用。
接下来,我们将向每个用户显示一个表单,用来获得信用卡详细信息,此过程中,我们调用了output_fns.php函数库中的display_card_form()函数。
