30.4 定义脚本架构
与前一个项目一样,对于这个项目,我们也采用了事件驱动的方法。该程序的架构保存在文件index.php中。该脚本有4个主要的部分,它们分别如下。
1.执行预处理:标题发送前必须完成的所有处理工作。
2.建立和发送标题:创建与发送HTML页的开始部分。
3.执行一个动作:响应已经传入的事件。正如前一个例子一样,事件包含在$action变量中。
4.发送页脚。
几乎所有的应用程序处理都是在这个文件中完成的。该程序还使用了表30-1中列出的函数库,正如前面所介绍的。
index.php脚本的所有代码如程序清单30-2所示。
程序清单30-2 index.php——金字塔式MLM的主要应用程序文件
<?php
/**
*Section 1:pre-processing
*/
include('include_fns.php');
session_start();
$action=$_GET['action'];
$buttons=array();
//append to this string if anything processed before header has output
$status='';
//need to process log in or out requests before anything else
if(($_POST['email'])&&($_POST['password'])){
$login=login($_POST['email'],$_POST['password']);
if($login=='admin'){
$status.="<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">
<strong>".get_real_name($_POST['email'])."</strong>
logged in successfully as
<strong>Administrator</strong>.</p>";
$_SESSION['admin_user']=$_POST['email'];
}else if($login=='normal'){
$status.="<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">
<strong>".get_real_name($_POST['email'])."</strong>
logged in successfully.</p>";
$_SESSION['normal_user']=$_POST['email'];
}else{
$status.="<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">Sorry,we could
not log you in with that email address
and password.</p>";
}
}
if($action=='log-out'){
unset($action);
$_SESSION=array();
session_destroy();
}
/**
*Section 2:set up and display headers
*/
//set the buttons that will be on the tool bar
if(check_normal_user()){
//if a normal user
$buttons[0]='change-password';
$buttons[1]='account-settings';
$buttons[2]='show-my-lists';
$buttons[3]='show-other-lists';
$buttons[4]='log-out';
}else if(check_admin_user()){
//if an administrator
$buttons[0]='change-password';
$buttons[1]='create-list';
$buttons[2]='create-mail';
$buttons[3]='view-mail';
$buttons[4]='log-out';
$buttons[5]='show-all-lists';
$buttons[6]='show-my-lists';
$buttons[7]='show-other-lists';
}else{
//if not logged in at all
$buttons[0]='new-account';
$buttons[1]='show-all-lists';
$buttons[4]='log-in';
}
if($action){
//display header with application name and description of page or action
do_html_header('Pyramid-MLM-'.format_action($action));
}else{
//display header with just application name
do_html_header('Pyramid-MLM');
}
display_toolbar($buttons);
//display any text generated by functions called before header
echo$status;
/**
*Section 3:perform action
*/
//only these actions can be done if not logged in
switch($action){
case'new-account':
//get rid of session variables
session_destroy();
display_account_form();
break;
case'store-account':
if(store_account($_SESSION['normal_user'],
$_SESSION['admin_user'],$_POST)){
$action='';
}
if(!check_logged_in()){
display_login_form($action);
}
break;
case'log-in':
case'':
if(!check_logged_in()){
display_login_form($action);
}
break;
case'show-all-lists':
display_items('All Lists',get_all_lists(),'information',
'show-archive','');
break;
case'show-archive':
display_items('Archive For'.get_list_name($_GET['id']),
get_archive($_GET['id']),'view-html',
'view-text','');
break;
case'information':
display_information($_GET['id']);
break;
}
//all other actions require user to be logged in
if(check_logged_in()){
switch($action){
case'account-settings':
display_account_form(get_email(),
get_real_name(get_email()),get_mimetype(get_email()));
break;
case'show-other-lists':
display_items('Unsubscribed Lists',
get_unsubscribed_lists(get_email()),'information',
'show-archive','subscribe');
break;
case'subscribe':
subscribe(get_email(),$_GET['id']);
display_items('Subscribed Lists',get_subscribed_lists(get_email()),
'information','show-archive','unsubscribe');
break;
case'unsubscribe':
unsubscribe(get_email(),$_GET['id']);
display_items('Subscribed Lists',get_subscribed_lists(get_email()),
'information','show-archive','unsubscribe');
break;
case'':
case'show-my-lists':
display_items('Subscribed Lists',get_subscribed_lists(get_email()),
'information','show-archive','unsubscribe');
break;
case'change-password':
display_password_form();
break;
case'store-change-password':
if(change_password(get_email(),$_POST['old_passwd'],
$_POST['new_passwd'],$_POST['new_passwd2'])){
echo"<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">OK:Password
changed.</p>";
}else{
echo"<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">Sorry,your
password could not be changed.</p>";
display_password_form();
}
break;
}
}
//The following actions may only be performed by an admin user
if(check_admin_user()){
switch($action){
case'create-mail':
display_mail_form(get_email());
break;
case'create-list':
display_list_form(get_email());
break;
case'store-list':
if(store_list($_SESSION['admin_user'],$_POST)){
echo"<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">New list added.</p>";
display_items('All Lists',get_all_lists(),'information',
'show-archive','');
}else{
echo"<p style=\"padding-bottom:50px\">List could not be
stored.Please try again.</p>";
}
break;
case'send':
send($_GET['id'],$_SESSION['admin_user']);
break;
case'view-mail':
display_items('Unsent Mail',get_unsent_mail(get_email()),
'preview-html','preview-text','send');
break;
}
}
/**
*Section 4:display footer
*/
do_html_footer();
?>
在以上程序清单中,可以看出代码4个部分清楚地标记出来了。在预处理阶段,我们将建立会话,并且完成在标题发送前必要的处理,在这个例子中,包括登录和登出。
在标题阶段,我们设置用户将会见到的菜单按钮,并且使用output_fns.php中的函数do_html_header()来显示相应的标题。该函数仅显示标题栏和菜单,我们将不详细介绍。
在脚本的主要部分,我们根据用户选择的操作做了相应的响应。这些操作分为3个子集:用户没有登录时可以进行的操作、普通用户可以进行的操作,以及管理员用户可以进行的操作。使用check_logged_in()和check_admin_user()函数来检查用户是否允许进行后两组操作。这3个函数都位于user_auth_fns.php函数库中。这些函数以及check_normal_user()函数的代码如程序清单30-3所示。
程序清单30-3 user_auth_fns.php中的函数——这些函数检查用户是否登录以及以什么级别登录
function check_normal_user(){
//see if somebody is logged in and notify them if not
if(isset($_SESSION['normal_user'])){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
function check_admin_user(){
//see if somebody is logged in and notify them if not
if(isset($_SESSION['admin_user'])){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
function check_logged_in(){
return(check_normal_user()||check_admin_user());
可以看到,这些函数使用会话变量normal_user和admin_user来检验用户是否登录。稍后,我们将讨论如何设置这些会话变量。
在该脚本的最后部分,我们使用output_fns.php中的函数do_html_footer()来发送HTML页脚。
我们简要地了解一下该系统中可能发生的动作,如表30-2所示。
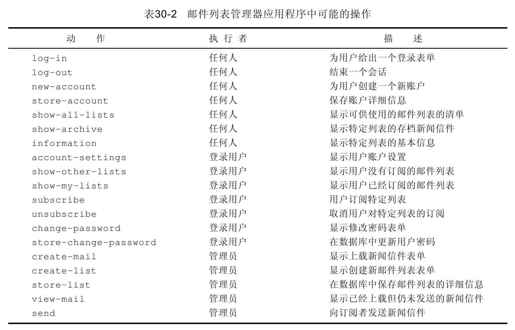
在这个表中,一个值得注意的省略是关于store-mail行的选项,即管理员通过create-mail动作上载输入新闻信件的操作。事实上,这个单独的功能是在另一个不同的文件upload.php中实现的。我们把它放在单独的一个文件中是为了减轻程序员对安全问题的注意。
在接下来的内容中,我们将讨论表30-2中给出的3组操作的实现,也就是,未登录用户的操作、登录用户的操作和管理员的操作。
