6.4.4 EAP-WSC处理流程分析
EAP-WSC流程涉及EAPOL中的四个状态机(SUPP_PAE、KEY_RX、SUPP_BE、Port Timers)以及EAP SM之间的联动。当STA成功关联到AP后,EAPOL及EAP状态机情况如下(详情请参考4.5.3节eapol_sm_notify_portEnabled分析)。
·SUPP_PAE为DISCONNECTED状态;
·KEY_RX为NO_KEY_RECEIVE状态;
·SUPP_BE为IDLE状态;
·EAP_SM为DISABLED状态。
根据图6-7所示,EAP-WSC流程的开始于STA向AP发送的EAPOL-Start帧。是什么原因导致STA发送EAPOL-Start帧呢?来看下文。
1.发送EAPOL-Start
在STA关联到AP流程的最后,eapol_sm_notify_portEnabled将设置portEnabled为1,根据代码(eapol_supp_sm.c中的SM_STEP(SUPP_PAE))以及图4-28可知,SUPP_PAE要进入的下一个状态是CONNECTING,其EA(Entry Aciton)代码如下。
[—>eapol_supp_sm.c::SM_STATE(SUPP_PAE,CONNECTING)]
- SM_STATE(SUPP_PAE, CONNECTING)
- {
- // SUPP_PAE_state此时的值为SUPP_PAE_DISCONNECTED,故send_start为0
- // 注意下面这个判断很重要,待会还会回到此处
- int send_start = sm->SUPP_PAE_state == SUPP_PAE_CONNECTING;
- SM_ENTRY(SUPP_PAE, CONNECTING);
- if (send_start) {
- sm->startWhen = sm->startPeriod;
- sm->startCount++;
- } else {
- #ifdef CONFIG_WPS //
- sm->startWhen = 1; // 注意,如果WPAS支持WPS,则startWhen值为1
- #else /* CONFIG_WPS */
- sm->startWhen = 3;
- #endif /* CONFIG_WPS */
- }
- // 启动Port Timers SM,Port Timers SM将递减startWhen,并调用eapol_sm_step以重新遍历状态机
- eapol_enable_timer_tick(sm);
- sm->eapolEap = FALSE; ..
- // 由于send_start为0,所以此时还不会发送EAPOL-Start包
- if (send_start) eapol_sm_txStart(sm);
- }
根据代码中的注释,当Port Timers SM运行时,它将递减startWhen变量(结果是startWhen的值变为0),然后通过eapol_sm_step重新遍历状态机。在该函数中,PAE的SM_STEP将被调用以检查是否需要进行状态切换,相关代码如下所示。
[—>eapol_supp_sm.c::SM_STEP(SUPP_PAE)]
- SM_STEP(SUPP_PAE)
- {
- ......// 略去不相关的内容
- else switch (sm->SUPP_PAE_state) { // SUPP_PAE_state还处于CONNECTING状态
- ......
- case SUPP_PAE_CONNECTING:
- if (sm->startWhen == 0 && sm->startCount < sm->maxStart)
- SM_ENTER(SUPP_PAE, CONNECTING);
- // 由于startWhen为0,PAE将重新进入CONNECTING状态
- ......
- break;
- case SUPP_PAE_AUTHENTICATING:
- ......
- }
- }
根据上面代码可知,PAE将再次从CONNECTING状态进入CONNECTING状态。请读者回顾SM_STATE(SUPP_PAE,CONNECTING)函数。这一次sendStart将取值1,所以eapol_sm_txStart会被调用,该函数的代码如下所示。
[—>eapol_supp_sm.c::eapol_sm_txStart]
- static void eapol_sm_txStart(struct eapol_sm *sm)
- {
- // eapol_send函数指针指向wpa_supplicant_eapol_send
- // 相关代码在wpas_glue.c中,请读者自行阅读
- sm->ctx->eapol_send(sm->ctx->eapol_send_ctx,
- IEEE802_1X_TYPE_EAPOL_START, (u8 *) "", 0);
- sm->dot1xSuppEapolStartFramesTx++;
- sm->dot1xSuppEapolFramesTx++;
- }
由上述代码可知,eapol_send的实例wpa_supplicant_eapol_send将最终发送EAPOL-Start帧。
2.状态机切换处理
STA发出EAPOL-Start后,AP将发送EAP-Request/Identity包。STA处理EAP-Request/Identity后将回复EAP-Response/Identity包。上述流程将触发EAPOL中的PAE、BE和EAP状态机联动。此联动过程相当复杂。故本节将以EAP-Request/Identity为入口,分析WPAS中状态机的切换处理。
注意 此处的状态机联动实际上反映的是WPAS中EAP包处理的通用流程。学习过程中,请读者务必结合4.4节EAP和EAPOL模块的理论知识。
先来看EAP-Request的处理。WPAS中,EAP包接收的函数是wpa_supplicant_rx_eapol(相关分析请参考4.5.3节分析EAPOL-Key交换流程时对wpa_supplicant_rx_eapol的介绍),我们说过非PSK认证方法将由eapol_sm_rx_eapol处理,故直接来看eapol_sm_rx_eapol函数,代码如下所示。
[—>eapol_supp_sm.c::eapol_sm_rx_eapol]
- int eapol_sm_rx_eapol(struct eapol_sm *sm, const u8 *src, const u8 *buf, size_t len)
- {
- const struct ieee802_1x_hdr *hdr; const struct ieee802_1x_eapol_key *key;
- int data_len; int res = 1; size_t plen;
- sm->dot1xSuppEapolFramesRx++;
- hdr = (const struct ieee802_1x_hdr *) buf;
- sm->dot1xSuppLastEapolFrameVersion = hdr->version;
- os_memcpy(sm->dot1xSuppLastEapolFrameSource, src, ETH_ALEN);
- plen = be_to_host16(hdr->length);
- ......
- #ifdef CONFIG_WPS
- /*
- workaround意思为“变通方案”。在WPAS中,它表示为了兼容某些AP的错误行为(例如发送的EAP包
- 格式不符合要求),而采用绕过去的方法来处理。
- */
- if (sm->conf.workaround && plen < len - sizeof(*hdr) &&
- hdr->type == IEEE802_1X_TYPE_EAP_PACKET &&
- len - sizeof(*hdr) > sizeof(struct eap_hdr)) {
- ......
- }
- #endif
- data_len = plen + sizeof(*hdr);
- switch (hdr->type) {
- case IEEE802_1X_TYPE_EAP_PACKET: // 本例中收到的是EAP-Request包,满足此case条件
- ......
- wpabuf_free(sm->eapReqData);
- sm->eapReqData = wpabuf_alloc_copy(hdr + 1, plen);
- if (sm->eapReqData) {
- sm->eapolEap = TRUE; // 设置条件变量
- eapol_sm_step(sm); // 触发状态机运行
- }
- break;
- ......
- }
- return res;
- }
WPAS每收到一个EAP包都会触发上述代码中的流程。回顾eapol_sm_step中和状态机运转相关的代码。
[—>eapol_supp_sm.c::eapol_sm_step]
- {
- int i;
- for (i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
- sm->changed = FALSE;
- SM_STEP_RUN(SUPP_PAE); // 先执行SUPP_PAE状态机
- SM_STEP_RUN(KEY_RX); // 再运转KEY_RX状态机
- SM_STEP_RUN(SUPP_BE); // 最后运转SUPP_BE状态机
- if (eap_peer_sm_step(sm->eap)) // 执行EAP_SM状态机
- sm->changed = TRUE;
- if (!sm->changed)
- break;
- }
- ......
- }
其中,eap_peer_sm_step的代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::eap_peer_sm_step]
- int eap_peer_sm_step(struct eap_sm *sm)
- {
- int res = 0;
- do { // 无限循环,直到EAP SM稳定后才退出
- sm->changed = FALSE;
- SM_STEP_RUN(EAP);
- if (sm->changed)
- res = 1;
- } while (sm->changed);
- return res;
- }
通过上述代码可知,EAPOL和EAP的状态机联动过程如下。
EAPOL先按顺序遍历PAE、KEY_RX、BE状态机,然后执行EAP状态机。只有EAP SM稳定后(即eap_peer_sm_step函数中的sm->changed为FALSE时)才退出eap_peer_sm_step。
如果上述四个状态机有任何一个状态机的状态不稳定(即sm->changed为TRUE),则继续遍历所有状态机。
特别需要指出的是,状态机A运行时可能会修改一些条件变量从而导致状态机B发生状态切换。虽然第4章对每个状态机的状态切换图都有详细介绍,但读者很难理清楚状态机之间是如何互相影响的。在此,笔者整理了WPAS从发送EAPOL-Start包到接收EAP-Request/Identity以及回复EAP-Response/Identity这一过程中四个状态机的切换过程,如图6-34所示。
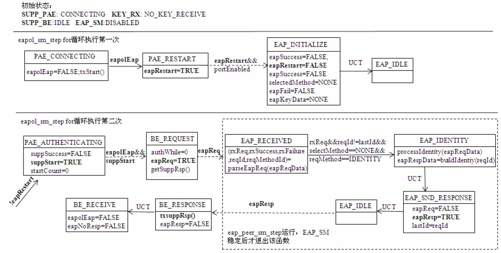
图6-34 EAP-Request/Response Identity流程中的状态机联动
图6-34中第一行显示了PAE、KEY_RX、BE和EAP_SM的初始状态。由于EAP-WSC不会收发EAPOL-Key帧,所以KEY_RX将不参与联动过程。
图中的方框上部所示为状态机以及当前的状态,格式为“状态机名_状态名”,如PAE_CONNECTING等。方框下部所示为该状态机对应状态的EA处理(由于篇幅原因,图中EA仅列出了一些重要的处理逻辑)。
当状态机A从一个状态切换到另一个状态时,切换过程用实箭头表示(例如第二行中,PAE_CONNECTING切换到PAE_RESTART,切换条件是“eapolEap为TRUE”。当WPAS收到一个EAP帧时,该变量将在上文介绍的eapol_sm_rx_eapol函数中被设置为TRUE)。
当状态机A在其EA处理中修改了某些条件变量(或者外界设置了某个条件变量)导致状态机B发生状态切换时,其切换过程用虚箭头表示。例如第二行中的PAE_RESTART状态,其EA将设置eapRestart为TRUE,而该条件和portEnabled将共同促使EAP_SM进入INITILIAZE状态。
第二行表示eapol_sm_step第一次循环过程中的状态机切换以处理接收到的EAP-Request/Identity包。但这一轮还不会真正处理EAP包。
第三行表示eapol_sm_step的第二次循环。在这次循环过程中,EAP状态机将处理EAP-Request/Identity包。在解析该包时,发现它包含了Identity信息,所以EAP SM将进入IDENTITY状态去处理它。处理完毕后,EAP SM将构造一个EAP-Response/Identity包,并设置eapResp变量为TRUE。
第三行中,eapResp变量将使得BE进入RESPONSE状态,该状态的EA将调用txsuppResp发送这个EAP-Response/Identity包。
当图6-34执行完毕后,EAPOL和EAP状态机将进入稳定状态,这样,eapol_sm_step得以返回。根据EAP-WSC的流程,WPAS下一步将继续接收并处理EAP包。在这以后的过程中(M1~M8),PAE保持Authenticating状态不变。
当EAPOL收到一个EAP包后,BE将从RECEIVE状态切换至REQUEST状态。EAP将根据EAP包的信息从IDLE状态转移到其他状态(首先是RECEIVED状态,在该状态中将解析EAP包的内容,根据内容以进入GET_METHOD或METHOD状态以处理EAP包)。
EAP状态机处理完EAP包,BE将进入RESPONSE状态并发送EAP回复包。整个流程将反复执行,直到EAP-WSC流程终结。
所以,对EAP-WSC流程来说,EAPOL状态机的执行过程比较固定。而对EAP SM来说,它将根据EAP包内容的不同而转移到不同的状态。下面我们将直接进入EAP对应的状态以分析不同EAP包的处理过程。
注意 根据图4-21关于EAP SM的描述,当portEnabled值为TRUE时,应该从DISABLED状态切换至INITIALIZE状态。不过,4.5.3节“wpa_supplicant_associate分析之三”中曾提到,由于force_disabled变量为TRUE,EAP_SM是无法转入INITIALIZED状态的。为什么此处它却可以呢?原来。由于本例使用的key_mgmt是WPA_KEY_MGMT_WPS,所以force_disabled变量将被设置为FALSE,这样EAP SM就可以转换至INITIALIZE状态了。其间的细节内容请读者参考wpa_supplicant_initiate_eapol及内部所调用的eapol_sm_notify_config函数。
3.EAP-Request/Identity处理
EAP状态机的RECEIVED状态将对收到的EAP包进行解析,相关代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::SM_STATE(EAP,RECEIVED)]
- SM_STATE(EAP, RECEIVED)
- {
- const struct wpabuf *eapReqData;
- SM_ENTRY(EAP, RECEIVED);
- eapReqData = eapol_get_eapReqData(sm);
- eap_sm_parseEapReq(sm, eapReqData);// 解析收到的EAP包
- sm->num_rounds++;
- }
eap_sm_parseEapReq的代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::eap_sm_parseEapReq]
- static void eap_sm_parseEapReq(struct eap_sm *sm, const struct wpabuf *req)
- {
- const struct eap_hdr *hdr; size_t plen; const u8 *pos;
- ......
- hdr = wpabuf_head(req);
- plen = be_to_host16(hdr->length);
- ......
- sm->reqId = hdr->identifier;
- if (sm->workaround) {...... }
- switch (hdr->code) {
- case EAP_CODE_REQUEST:
- ......
- sm->rxReq = TRUE;
- pos = (const u8 *) (hdr + 1);
- sm->reqMethod = *pos++; // 对于EAP-Request Identity包而言,reqMethod=1
- // 处理EAP-Request/WSC_Start,WSC_Start属于扩展EAP协议
- // 此处收到的是Identity包,所以下面这个if条件并不满足
- if (sm->reqMethod == EAP_TYPE_EXPANDED) {
- ......//
- // 对于EAP-Request/WSC_Start而言,reqVendor取值为0x0372a
- sm->reqVendor = WPA_GET_BE24(pos);
- pos += 3;
- // 获取Vendor Type,值为0x1,表示SimpleConfig。请参考图6-22
- sm->reqVendorMethod = WPA_GET_BE32(pos);
- }
- break;
- case EAP_CODE_RESPONSE:
- ......
- break;
- case EAP_CODE_SUCCESS:
- sm->rxSuccess = TRUE;
- break;
- case EAP_CODE_FAILURE:
- sm->rxFailure = TRUE; // 在EAP-WSC流程的最后,AP将发送EAP-Failure包
- break;
- ......
- }
- }
根据图6-34所示,EAP SM接着将进入IDENTITY状态(读者可参考eap.c中的eap_peer_sm_step_local函数),代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::SM_STATE(EAP,IDENTITY)]
- SM_STATE(EAP, IDENTITY)
- {
- const struct wpabuf *eapReqData;
- SM_ENTRY(EAP, IDENTITY);
- eapReqData = eapol_get_eapReqData(sm);// 获取EAP-Request包内容
- eap_sm_processIdentity(sm, eapReqData);// 处理Identity,请读者自行阅读此函数
- wpabuf_free(sm->eapRespData);
- sm->eapRespData = NULL;
- // 构造EAP-Response Identity包
- sm->eapRespData = eap_sm_buildIdentity(sm, sm->reqId, 0);
- }
来看看eap_sm_buildIdentity函数,代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::eap_sm_buildIdentity]
- struct wpabuf * eap_sm_buildIdentity(struct eap_sm *sm, int id, int encrypted)
- {
- /*
- 获取wpa_ssid中的eap_peer_config对象,它代表EAP配置信息。该eap_peer_config的来历请
- 读者自行阅读wpa_supplicant_initiate_eapol及内部所调用的eapol_sm_notify_config函数。
- 总之,下面这个config对象将指向“WPS_PIN any”命令处理时创建的wpa_ssid中eap变量,它指向
- 一个eap_peer_config实例。
- eap_get_config内部将通过函数指针调用eap_supp_sm.c中的eapol_sm_get_config函数。
- */
- struct eap_peer_config *config = eap_get_config(sm);
- struct wpabuf *resp; const u8 *identity; size_t identity_len;
- if (config == NULL) { ......}
- if (sm->m && sm->m->get_identity && .......) .......
- else if (!encrypted && config->anonymous_identity)......
- else {
- // 对WSC来说,identity的值为“WFA-SimpleConfig-Enrollee-1-0”
- identity = config->identity;
- identity_len = config->identity_len;
- }
- if (identity == NULL) {
- ......// 没有配置identity
- } else if (config->pcsc) { ......}
- // 构造EAP-Response/Identity回复包
- resp = eap_msg_alloc(EAP_VENDOR_IETF, EAP_TYPE_IDENTITY, identity_len,
- EAP_CODE_RESPONSE, id);
- ......
- wpabuf_put_data(resp, identity, identity_len);
- return resp;
- }
EAP-Request/Identity的处理流程比较简单,此处就不再详述。当AP收到来自STA的EAP-Response/Identity后,它将发送EAP-Request/WSC_Start帧。该帧将导致EAP SM进入GET_METHOD状态,马上来看相关代码。
4.EAP-Request/WSC_Start处理
图6-35所示为EAP-Request/WSC_Start帧的内容。
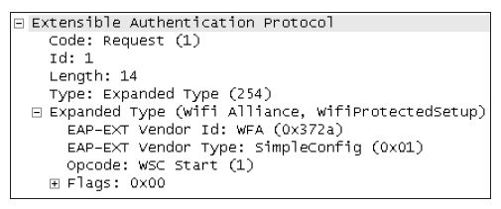
图6-35 EAP-Request/WSC_Start示例
首先处理该帧的是EAP_SM GET_METHOD状态,相关代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::SM_STATE(EAP,GET_METHOD)]
- SM_STATE(EAP, GET_METHOD)
- {
- int reinit;
- EapType method;
- SM_ENTRY(EAP, GET_METHOD);
- if (sm->reqMethod == EAP_TYPE_EXPANDED) method = sm->reqVendorMethod;
- else method = sm->reqMethod;
- /*
- 判断WPAS是否支持此vendor对应的方法。reqVendor的值为0x372a。在4.3.2节
- “eap_register_methods分析”中,WPAS支持的各种EAP方法将通过在eap_register_methods
- 函数中被注册,其中就有EAP-WSC方法。
- */
- if (!eap_sm_allowMethod(sm, sm->reqVendor, method)) goto nak;
- ......
- sm->selectedMethod = sm->reqMethod; // selectedMethod值为EAP_TYPE_EXPANDED(值为254)
- if (sm->m == NULL)// sm->m指向一个eap_method对象,它代表一种特定的EAP算法
- sm->m = eap_peer_get_eap_method(sm->reqVendor, method);
- // 获取EAP-WSC算法模块对应的对象
- if (!sm->m) goto nak;
- sm->ClientTimeout = EAP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;
- if (reinit) ......
- else
- sm->eap_method_priv = sm->m->init(sm); // 初始化EAP-WSC算法
- if (sm->eap_method_priv == NULL) {...... // 错误处理}
- sm->methodState = METHOD_INIT;
- return;
- ......
- }
EAP-WSC算法的注册代码位于eap_peer_wsc_register函数(位于eap_wsc.c,请读者自行阅读)中,它为EAP-WSC模块定制了三个函数。
·eap_wsc_init和eap_wsc_deinit:用于EAP-WSC算法模块资源的初始化和释放。
·eap_wsc_process:处理EAP-WSC包(即类型为WSC_MSG的包)。
提示 EAP-WSC的初始化函数比较简单,请读者自行研读eap_wsc_init函数。
GET_METHOD之后,EAP SM下一个进入的状态是METHOD,其代码如下所示。
[—>eap.c::SM_STATE(EAP,METHOD)]
- SM_STATE(EAP, METHOD)
- {
- struct wpabuf *eapReqData; struct eap_method_ret ret;
- SM_ENTRY(EAP, METHOD);
- ......
- eapReqData = eapol_get_eapReqData(sm); // 先获得请求信息
- os_memset(&ret, 0, sizeof(ret));
- ret.ignore = sm->ignore; ret.methodState = sm->methodState;
- ret.decision = sm->decision; ret.allowNotifications = sm->allowNotifications;
- wpabuf_free(sm->eapRespData);
- sm->eapRespData = NULL;
- // 对WSC来说,process函数为eap_wsc_process
- sm->eapRespData = sm->m->process(sm, sm->eap_method_priv, &ret, eapReqData);
- ......// 其他处理
- }
- }
由上面的代码可知,对于EAP-WSC算法来说,process真正的实现是eap_wsc_process,下面将详细介绍。
5.eap_wsc_process介绍
eap_wsc_process的代码如下所示。
[—>eap_wsc.c::eap_wsc_process]
- static struct wpabuf * eap_wsc_process(struct eap_sm *sm, void *priv,
- struct eap_method_ret *ret,const struct wpabuf *reqData)
- {
- struct eap_wsc_data *data = priv; const u8 *start, *pos, *end;
- size_t len; u8 op_code, flags, id; u16 message_length = 0;
- enum wps_process_res res; struct wpabuf tmpbuf;
- struct wpabuf *r;
- // 校验EAP-WSC包的头部信息
- pos = eap_hdr_validate(EAP_VENDOR_WFA, EAP_VENDOR_TYPE_WSC, reqData, &len);
- ......
- op_code = *pos++; // 获取OpCode
- flags = *pos++; // 获取标志位
- if (flags & WSC_FLAGS_LF) {......// LF标志位处理}
- if (data->state == WAIT_FRAG_ACK) { ......// MF标志位处理}
- // 消息类型检查。当前EAP-WSC模块的状态是WAIT_START
- if (data->state == WAIT_START) {
- ......// 检查类型
- eap_wsc_state(data, MESG); // 设置EAP-WSC的状态
- goto send_msg; // 直接跳转到send_msg
- } else if (op_code == WSC_Start) {
- ret->ignore = TRUE;
- return NULL;
- }
- ......
- if (flags & WSC_FLAGS_MF) {......// 分片处理}
- ......
- // 关键函数①wps_process_msg
- res = wps_process_msg(data->wps, op_code, data->in_buf);
- switch (res) {
- case WPS_DONE:
- eap_wsc_state(data, FAIL);
- break;
- ......// WPS_CONTINUE,WPS_FAILURE和WPS_PENDING的处理
- }
- ......
- send_msg:
- if (data->out_buf == NULL) {
- data->out_buf = wps_get_msg(data->wps, &data->out_op_code);// 关键函数②
- ......
- }
- eap_wsc_state(data, MESG); //
- r = eap_wsc_build_msg(data, ret, id);// 构造用于回复的EAP-WSC消息包
- ......
- return r;
- }
eap_wsc_process中有两个关键函数。
·wps_process_msg:对于Enrollee来说,其内部将调用wps_enrollee_process_msg以处理接收到的EAP-WSC_MSG消息,例如M2、M4、M6、M8等消息。
·wps_get_msg:对于Enrollee来说,其内部将调用wps_enrollee_get_msg以构造M1、M3、M5、M7、WSC_Done等消息。
我们在前面已经介绍过M1~M8的内容。在WAPS的代码中,这部分内容也比较简单,所以本节不展开详细讨论。下面将介绍WPAS如何处理M8消息中的Credentials属性集。毕竟,EAP-WSC算法的目的就是为了得到这个Credentials属性集。
6.M8消息处理
M8消息的处理函数是wps_process_m8,相关代码如下所示。
[—>wps_enrollee.c::wps_process_m8]
- static enum wps_process_res wps_process_m8(struct wps_data *wps, const struct wpabuf *msg,
- struct wps_parse_attr *attr)
- {
- struct wpabuf *decrypted;
- struct wps_parse_attr eattr;
- ......
- // 比较接收到的Enrollee Nonce和Authenticator的内容,防止被中间人篡改
- if (wps_process_enrollee_nonce(wps, attr->enrollee_nonce) ||
- wps_process_authenticator(wps, attr->authenticator, msg)) {
- wps->state = SEND_WSC_NACK;
- return WPS_CONTINUE;
- }
- ......
- // 解密Encrypted Settings属性集合
- decrypted = wps_decrypt_encr_settings(wps, attr->encr_settings, attr->encr_settings_len);
- // 校验
- if (wps_validate_m8_encr(decrypted, wps->wps->ap,attr->version2 != NULL) < 0) {
- ......// 错误处理
- }
- // 解析Encrypted Settings属性集合中携带的属性信息
- if (wps_parse_msg(decrypted, &eattr) < 0 ||
- wps_process_key_wrap_auth(wps, decrypted, eattr.key_wrap_auth) ||
- wps_process_creds(wps, eattr.cred, eattr.cred_len,eattr.num_cred,
- attr->version2 != NULL) || wps_process_ap_settings_e(wps, &eattr, decrypted,
- attr->version2 != NULL)) {......// 错误处理}
- wpabuf_free(decrypted);
- wps->state = WPS_MSG_DONE;
- return WPS_CONTINUE;
- }
上面代码中:
·wps_decrypt_encr_settings先解密Encrpyted Settings属性,解密后的内容保存在decrypted变量中,decrypted是一块内存缓冲。
·然后调用wps_parse_msg来解析decrypted缓冲。根据6.2.3节对M7和M8的介绍,Encrypted Settings包含一系列属性。
·调用wps_process_creds处理Encyrpted Settings中的Credentials属性集。该属性集的内容可参考表6-6。
wps_process_creds的代码如下所示。
[—>wps_enrollee.c::wps_process_creds]
- static int wps_process_creds(struct wps_data *wps, const u8 *cred[],
- size_t cred_len[], size_t num_cred, int wps2)
- {
- size_t i;
- int ok = 0;
- .......
- for (i = 0; i < num_cred; i++) {
- int res;
- res = wps_process_cred_e(wps, cred[i], cred_len[i], wps2);
- // 处理属性集中的每一项属性
- if (res == 0) ok++;
- .......
- }
- ......
- return 0;
- }
wps_process_cred_e函数的最后将通过cred_cb回调函数将属性传递给wpa_supplicant。该回调函数在6.4.3节WSC模块初始化分析时介绍的wpas_wps_init函数中被设置为wpa_supplicant_wps_cred,而此函数的代码如下所示。
[—>wps_supplicant.c::wpa_supplicant_wps_cred]
- static int wpa_supplicant_wps_cred(void *ctx,const struct wps_credential *cred)
- {
- struct wpa_supplicant *wpa_s = ctx;
- struct wpa_ssid *ssid = wpa_s->current_ssid;
- u8 key_idx = 0; u16 auth_type;
- ......
- /*
- wps_cred_processing默认为0,表示WPAS内部处理credentials信息。值为1表示将credentials
- 等信息将通过ctrl_iface发送给客户端去处理。值为2表示credentials信息由WPAS内部处理,但也会发送
- 给客户端。
- */
- if (wpa_s->conf->wps_cred_processing == 1) return 0;
- auth_type = cred->auth_type; // 获取AP的认证算法
- if (auth_type == (WPS_AUTH_WPAPSK | WPS_AUTH_WPA2PSK)) auth_type = WPS_AUTH_WPA2PSK;
- // 检查认证算法设置是否正确
- if (auth_type != WPS_AUTH_OPEN && auth_type != WPS_AUTH_SHARED &&
- auth_type != WPS_AUTH_WPAPSK && auth_type != WPS_AUTH_WPA2PSK) return 0;
- // EAP-WSC工作基本完成,此时需要更新wpa_ssid对象的信息
- if (ssid && (ssid->key_mgmt & WPA_KEY_MGMT_WPS)) {
- os_free(ssid->eap.identity);
- ssid->eap.identity = NULL ssid->eap.identity_len = 0;
- os_free(ssid->eap.phase1); ssid->eap.phase1 = NULL;
- os_free(ssid->eap.eap_methods); ssid->eap.eap_methods = NULL;
- if (!ssid->p2p_group)
- ssid->temporary = 0;
- }
- ......
- // 先恢复wpa_ssid的默认设置
- wpa_config_set_network_defaults(ssid);
- os_free(ssid->ssid);
- ssid->ssid = os_malloc(cred->ssid_len);
- if (ssid->ssid) {
- os_memcpy(ssid->ssid, cred->ssid, cred->ssid_len);
- ssid->ssid_len = cred->ssid_len;
- }
- // 结合属性信息,更新wpa_ssid中的各个项。首先更新加密算法设置
- switch (cred->encr_type) {
- ......
- case WPS_ENCR_TKIP:
- ssid->pairwise_cipher = WPA_CIPHER_TKIP;
- break;
- case WPS_ENCR_AES:
- ssid->pairwise_cipher = WPA_CIPHER_CCMP;
- break;
- }
- ......// 更新认证算法设置
- switch (auth_type) {
- case WPS_AUTH_OPEN:
- ssid->auth_alg = WPA_AUTH_ALG_OPEN;
- ssid->key_mgmt = WPA_KEY_MGMT_NONE;
- ssid->proto = 0;
- break;
- ......
- case WPS_AUTH_WPA2PSK:
- ssid->auth_alg = WPA_AUTH_ALG_OPEN;
- ssid->key_mgmt = WPA_KEY_MGMT_PSK;
- ssid->proto = WPA_PROTO_RSN;
- break;
- }
- if (ssid->key_mgmt == WPA_KEY_MGMT_PSK) {
- // 更新PSK
- if (cred->key_len == 2 * PMK_LEN) {
- if (hexstr2bin((const char *) cred->key, ssid->psk,PMK_LEN)) return -1;
- ssid->psk_set = 1;
- ssid->export_keys = 1;
- }......
- }
- // 处理某些使用混合加密模式的AP对WPS支持不够完善的情况
- wpas_wps_security_workaround(wpa_s, ssid, cred);
- #ifndef CONFIG_NO_CONFIG_WRITE
- if (wpa_s->conf->update_config && // 将配置信息写到配置文件中对应的无线网络项中
- wpa_config_write(wpa_s->confname, wpa_s->conf)) { ......}
- #endif /* CONFIG_NO_CONFIG_WRITE */
- return 0;
- }
图6-36所示为Galaxy Note 2最终所设置的无线网络配置信息。有了网络信息,当STA和AP断开后,它将使用新的网络信息向AP发起关联请求。这部分内容我们已经在第4章中重点介绍过了。

图6-36 WSC最终获取的无线网络配置信息
提示 请读者自行研究MSG_Done消息的构造,在那里WPAS将发送WPS-SUCCESS信息给上层的WifiMonitor。这样,WifiStateMachine才能收到WPS_SUCCESS_EVENT消息。
回顾整个EAP-WSC流程,从代码角度来说,该流程较难的部分不在EAP-WSC本身,而是在于状态机联动。读者不妨仔细阅读关于状态机切换处理部分,然后研究EAP-WSC的内容。
提示 建议读者自行研究WPAS代码中M1~M7的处理流程以加深对EAP-WSC的理解。
