第一个GUI程序
使用Tkinter十分简单,我们来编写一个GUI版本的“Hello, world!”。
第一步是导入Tkinter包的所有内容:
from tkinter import *
第二步是从 Frame 派生一个 Application 类,这是所有Widget的父容器:
class Application(Frame):
def init(self, master=None):
Frame.init(self, master)
self.pack()
self.createWidgets()
def createWidgets(self):
self.helloLabel = Label(self, text='Hello, world!')
self.helloLabel.pack()
self.quitButton = Button(self, text='Quit', command=self.quit)
self.quitButton.pack()
在GUI中,每个Button、Label、输入框等,都是一个Widget。Frame则是可以容纳其他Widget的Widget,所有的Widget组合起来就是一棵树。
pack() 方法把Widget加入到父容器中,并实现布局。 pack() 是最简单的布局, grid() 可以实现更复杂的布局。
在 createWidgets() 方法中,我们创建一个 Label 和一个 Button ,当Button被点击时,触发 self.quit() 使程序退出。
第三步,实例化 Application ,并启动消息循环:
app = Application()
# 设置窗口标题:
app.master.title('Hello World')
# 主消息循环:
app.mainloop()
GUI程序的主线程负责监听来自操作系统的消息,并依次处理每一条消息。因此,如果消息处理非常耗时,就需要在新线程中处理。
运行这个GUI程序,可以看到下面的窗口:
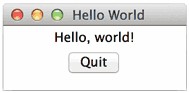
点击“Quit”按钮或者窗口的“x”结束程序。
